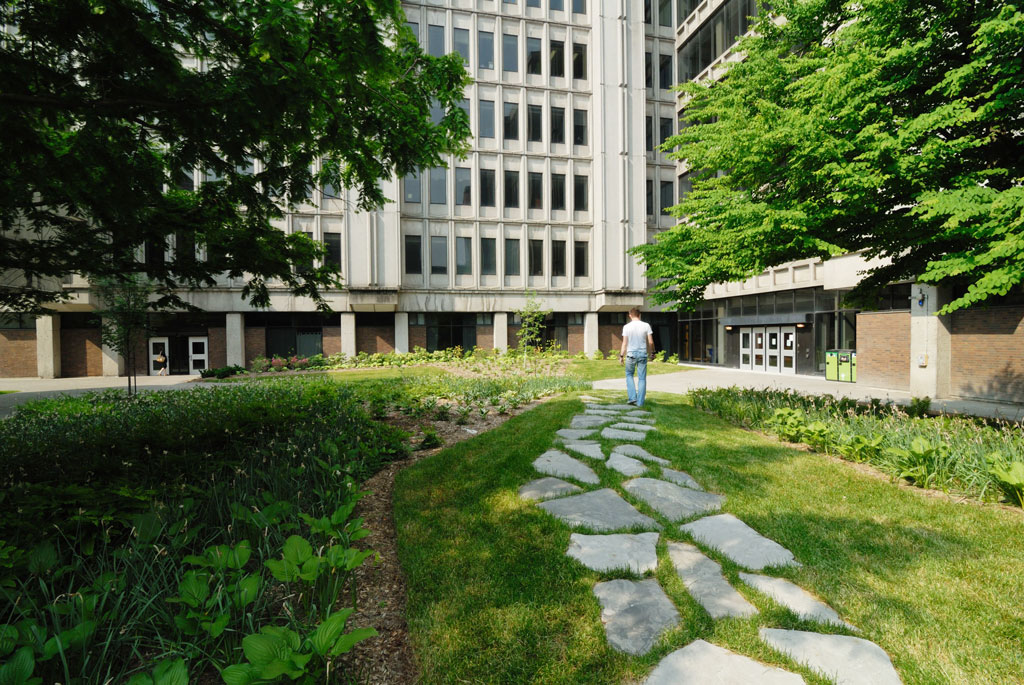
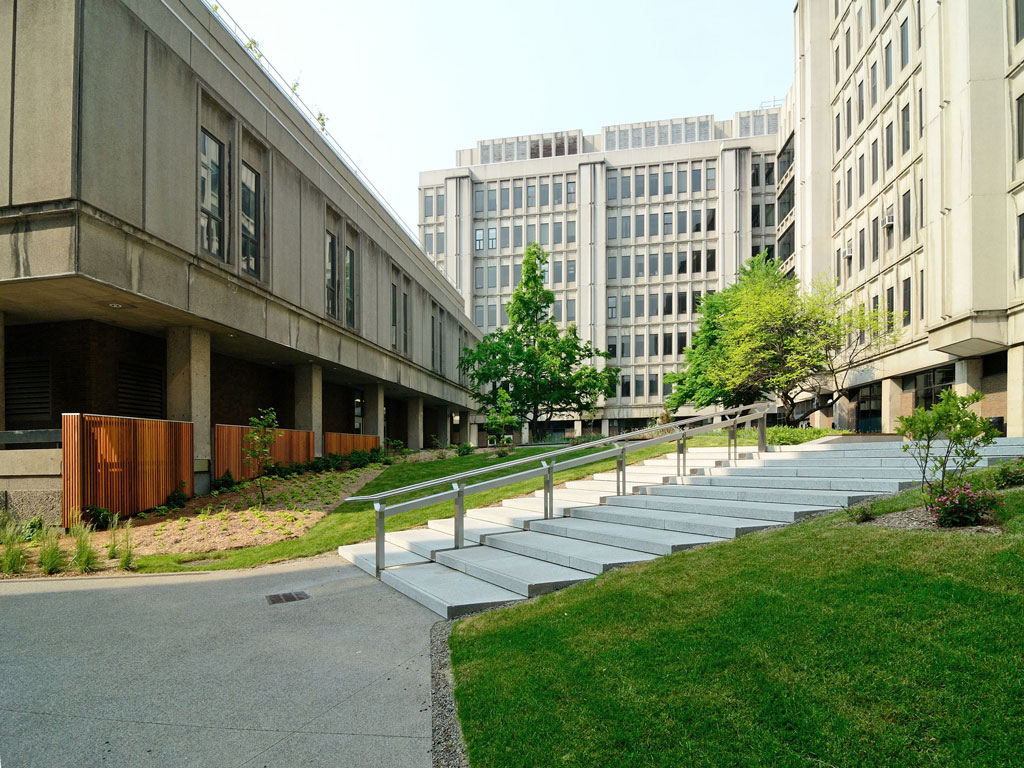
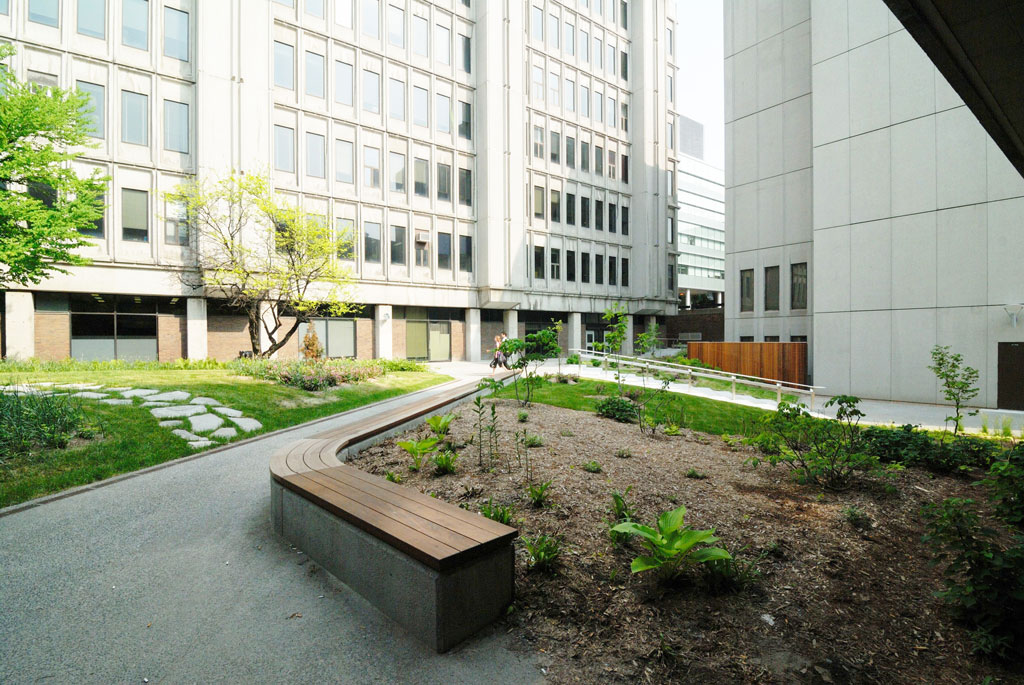
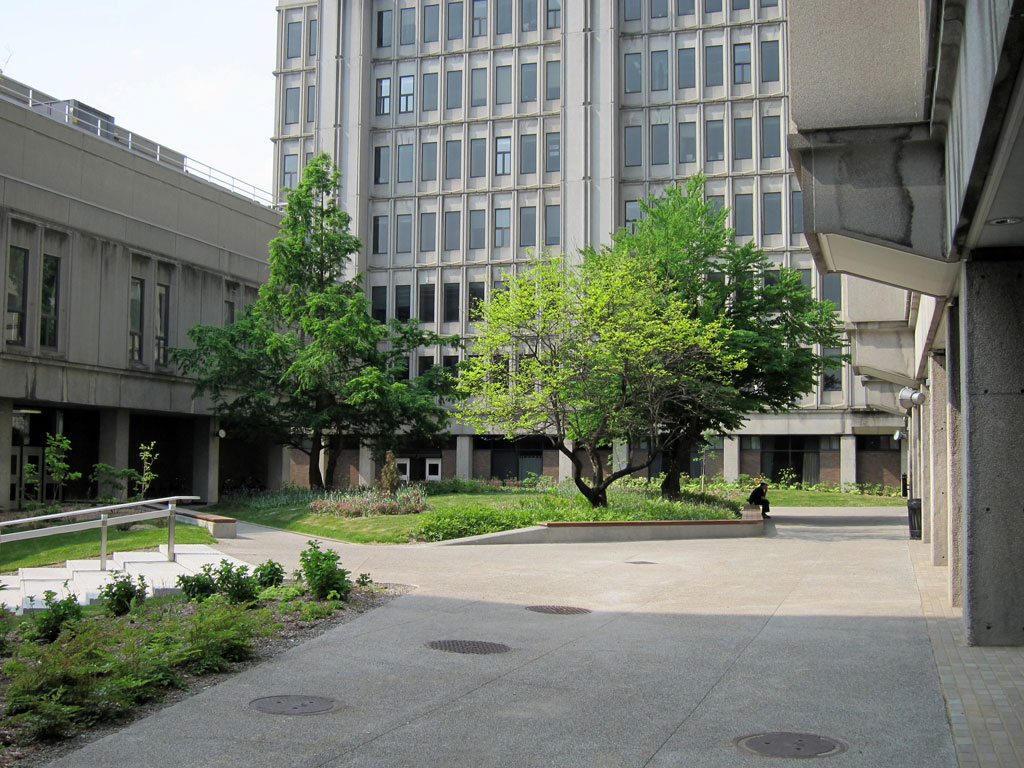
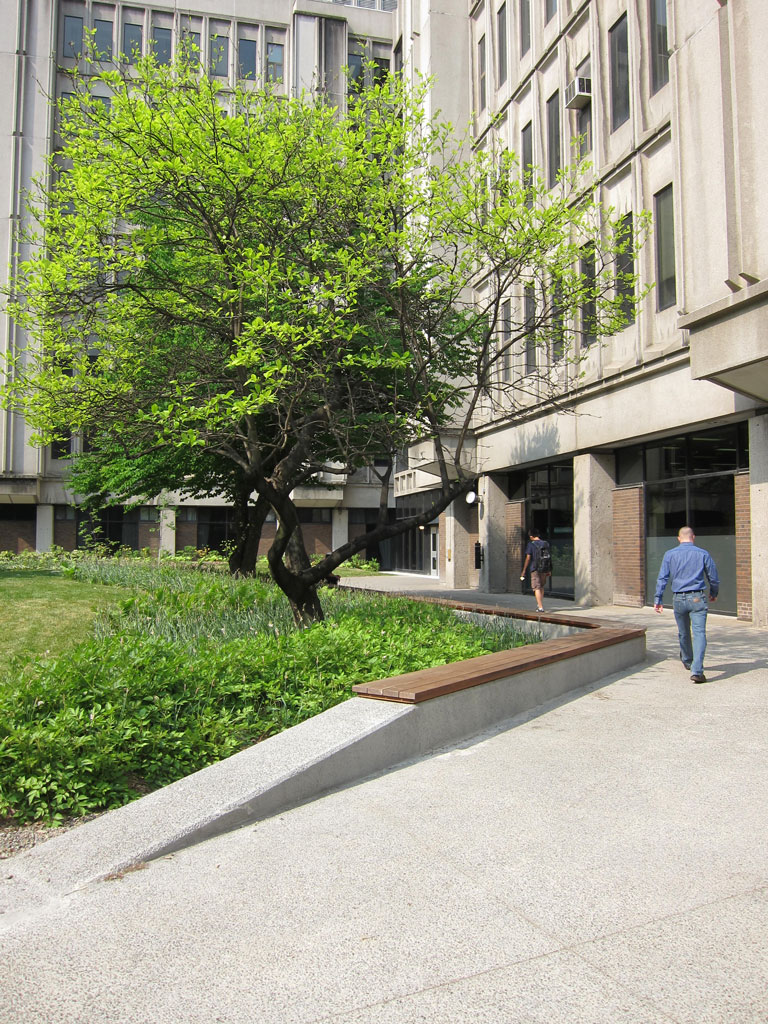
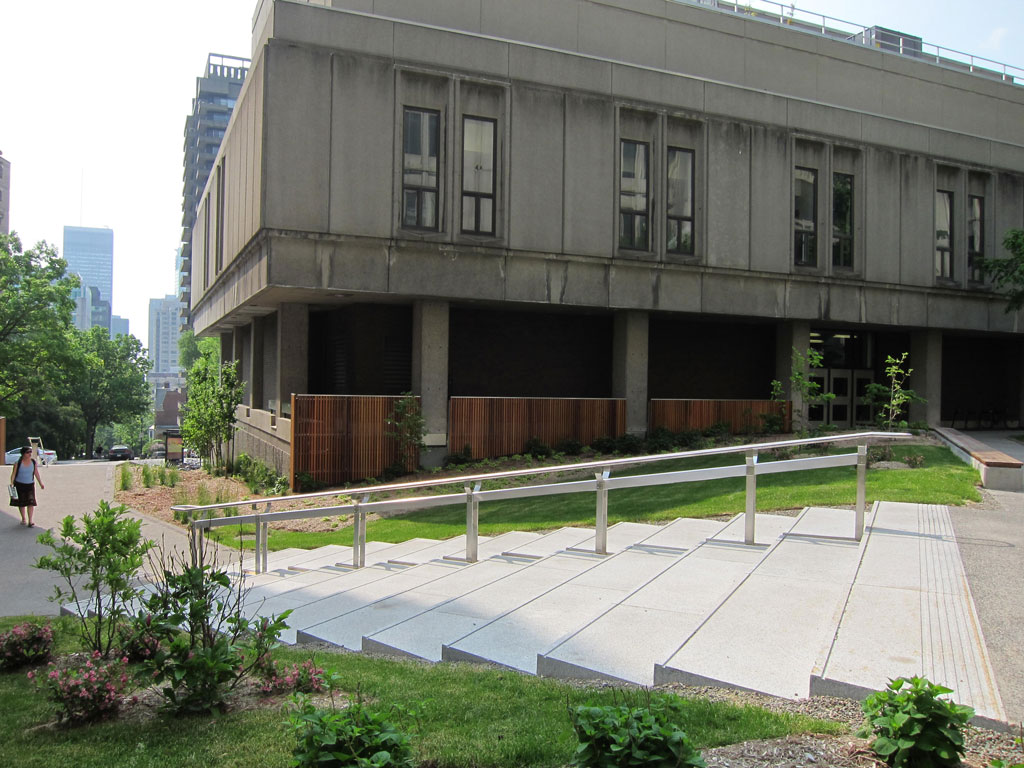
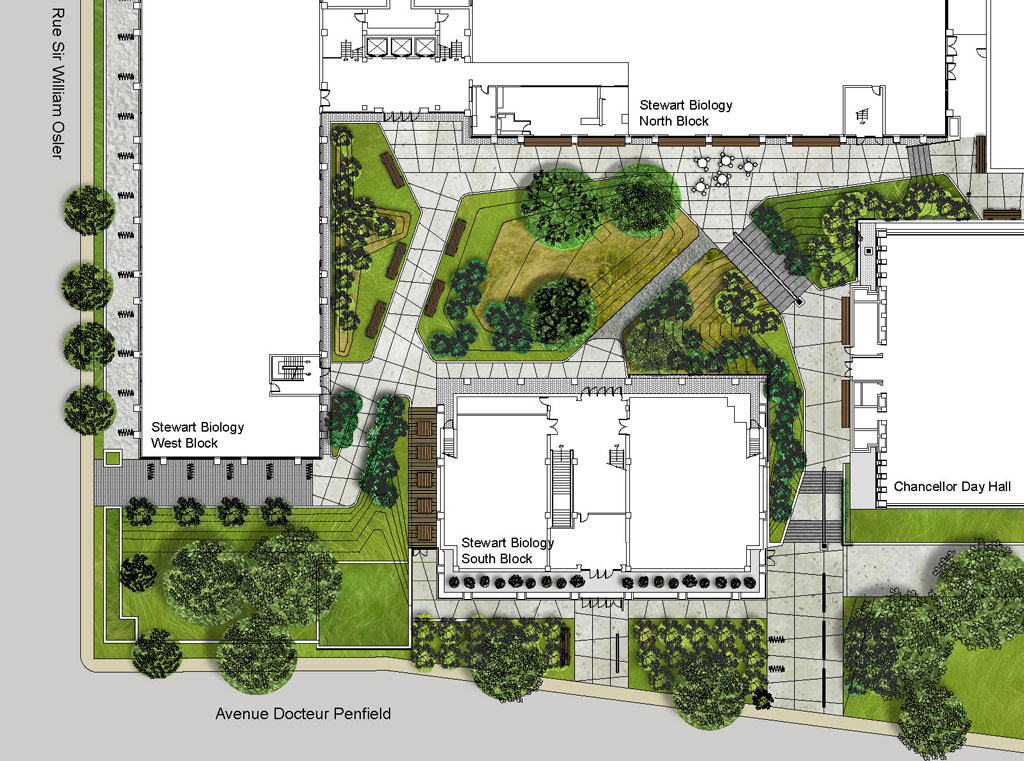
The terrace is a large central exterior space that connects the four pavilions of the Stewart Biology building at McGill University. The goal of the project was to transform the existing concrete space into a garden, a relaxing area, an outside study space and a meeting point. The new Stewart Biology Terrace has become a real public place, where logical paths cross each other and divide the fresh new grass and carefully selected plants.
About 9000 plants, including flowers, shrubs and trees were planted. The existing vegetation, including a rare Meta Sequoia, was conserved. The vegetation helps to offset the heat island effect thanks to effects of evapo-transpiration and shading. In addition, the green spaces help manage rainwater runoff.